The general law of expansion or compression of a perfect gas
is
PVn =
Constant
It gives the relationship between the pressure and volume of a
given quantity of gas. The value of n depends upon the nature
of the gas and condition under which the changes (i.e. expansion or
compression) takes place. The value of n may be between zero and
infinity. But the following values of n are important from the
subject point of view:
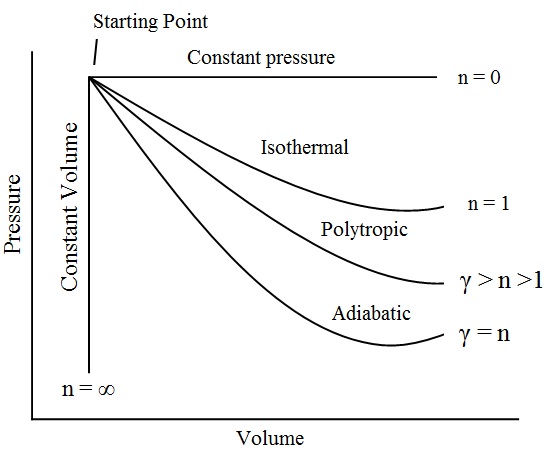
- When n=0, then PV0 = Constant, i.e. P = Constant. In other words, for the expansion or compression of a perfect gas at constant pressure, n=0.
- When n=1, then PV = Constant, i.e. the expansion or compression is iso-thermal or hyperbolic.
- When n lies between 1 and n, the expansion or compression is polytropic, i.e PVn = Constant.
- When n=γ, the expansion or compression is adiabatic, i.e PVγ = Constant.
- When n=∞, the expansion or compression is at constant volume, i.e V = Constant.








No comments:
Post a Comment